In the complex landscape of modern business operations, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) programs stand as integral tools that integrate various business functions into a unified platform. This article explores the key aspects of ERP programs and their impact on business management.
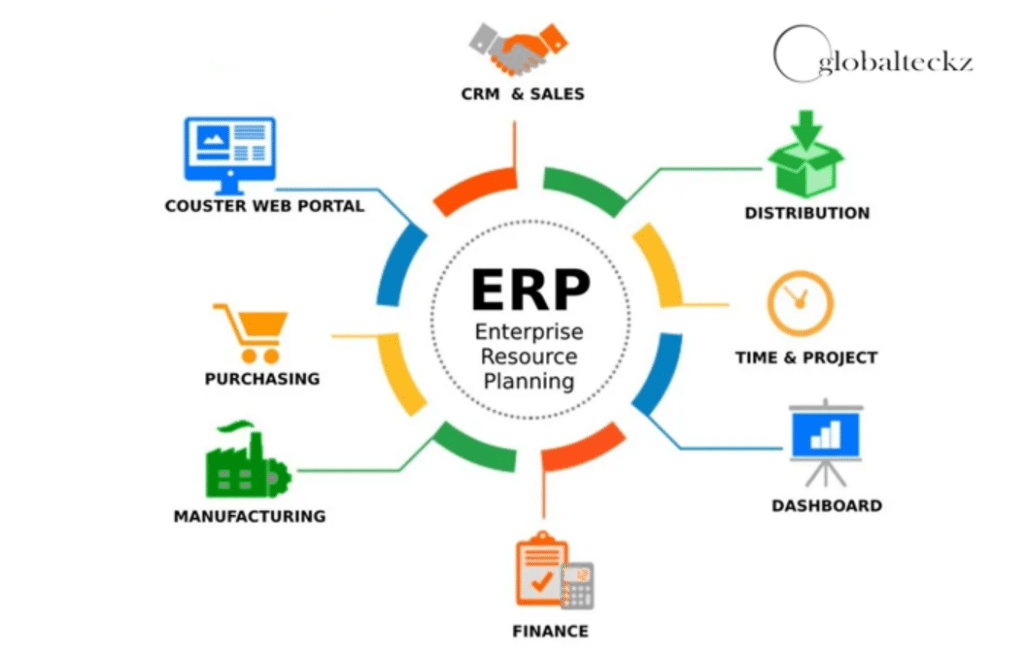
Core Components and Modules of ERP Programs
Financial Management
ERP programs include robust financial management modules, covering aspects such as accounts payable, accounts receivable, budgeting, and financial reporting. This ensures accurate and transparent financial operations.
Human Resources
Human Resources modules in ERP programs manage employee data, payroll, performance evaluations, and training. This centralized approach streamlines HR processes, fostering a more efficient workforce management system.
Supply Chain Management
The Supply Chain Management module optimizes procurement, production planning, and inventory control. ERP programs enhance visibility and coordination throughout the supply chain, reducing lead times and operational costs.
Advantages of ERP Programs for Businesses
Streamlined Business Processes
ERP programs streamline business processes by integrating different functions into a cohesive system. This leads to improved efficiency, reduced manual errors, and enhanced overall productivity.
Improved Data Accuracy
Centralized data management in ERP programs minimizes data duplication and discrepancies. This results in improved data accuracy, providing decision-makers with reliable information for strategic planning.
Enhanced Decision-Making
Real-time data access and comprehensive reporting tools empower decision-makers. ERP programs provide insights into various aspects of the business, enabling informed decision-making and strategic planning.
Integration Capabilities of ERP Programs
Seamless Integration Across Departments
ERP programs break down departmental silos by providing seamless integration across various business functions. This fosters collaboration, enhances communication, and ensures a holistic view of organizational operations.
Collaboration Tools
Built-in collaboration tools within ERP programs facilitate communication and cooperation among team members. Features like shared calendars, document management, and project tracking contribute to a more collaborative work environment.
ERP Program Implementation Best Practices
Thorough Needs Assessment
A thorough needs assessment is crucial before implementing an ERP program. Understanding the specific requirements of the business ensures that the chosen program aligns with organizational goals.
Comprehensive Training Programs
Successful implementation relies on comprehensive training programs for employees. Ensuring that users are proficient in utilizing the features of the ERP program minimizes resistance to change and maximizes its benefits.
Common Challenges and Solutions in ERP Program Implementation
Data Migration Challenges
Data migration can pose challenges during ERP program implementation. A meticulous data migration strategy and collaboration with experienced consultants help address issues and ensure a smooth transition.
Managing Resistance to Change
Resistance to change is a common challenge in ERP program implementation. Clear communication, involvement of key stakeholders, and providing ongoing support contribute to overcoming resistance.
Success Stories with ERP Programs
Case Study: Company W’s Transformation
Company W, a multinational corporation, witnessed a significant transformation after implementing an ERP program. The integration of financial management, human resources, and supply chain modules resulted in a 30% increase in overall operational efficiency.
Future Trends in ERP Programs
Cloud-Based Innovations
The future of ERP programs lies in cloud-based innovations. Cloud-based solutions offer increased accessibility, scalability, and flexibility, allowing businesses to adapt to evolving technological landscapes.
AI and Automation Integration
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and automation is a future trend in ERP programs. These technologies enhance data analysis, automate repetitive tasks, and contribute to more intelligent decision-making.
Choosing the Right ERP Program
Consideration of Industry-Specific Solutions
Choosing an ERP program tailored to the specific needs of the industry ensures optimal functionality. Industry-specific solutions address unique challenges and requirements.
Scalability and Flexibility
The right ERP program should be scalable to accommodate business growth and flexible enough to adapt to changing needs. This ensures a long-term solution that evolves with the organization.
Comparisons with Other Business Management Solutions
ERP vs. CRM
While ERP focuses on overall business management, Customer Relationship Management (CRM) is dedicated to customer interactions. Both are valuable but serve different purposes, with some overlap in functionalities.
ERP vs. MRP
Material Requirements Planning (MRP) focuses specifically on production planning and inventory management, while ERP covers a broader range of business functions. The choice depends on the organization’s specific needs.
ERP Program Pricing Models
Subscription-based Models
ERP programs commonly follow a subscription-based pricing model, offering businesses flexibility based on their size and needs. This eliminates the need for significant upfront investments and allows for scalable growth.
Additional Costs for Customization
While the base subscription covers essential functionalities, businesses requiring extensive customization may incur additional costs. Transparent communication with the ERP provider ensures a clear understanding of customization expenses.
Security Measures in ERP Programs
Data Encryption
Data encryption is a fundamental security measure in ERP programs. It safeguards sensitive information, ensuring that confidential data remains protected from unauthorized access.
Role-Based Access Control
ERP programs implement role-based access control, providing granular control over user access. This ensures that employees have access only to the information and functionalities necessary for their roles.
User Reviews and Testimonials
Positive Experiences
Users often commend ERP programs for their user-friendly interfaces, comprehensive features, and positive impact on business operations. The ability to centralize data and improve collaboration is frequently highlighted.
Areas for Improvement
Constructive feedback often revolves around the need for continuous improvement in user training and the interface. ERP providers’ commitment to addressing these concerns ensures ongoing enhancements.
Industry-Specific Applications
ERP Programs in Manufacturing
Manufacturing businesses benefit significantly from ERP programs, optimizing production schedules, managing inventory, and ensuring efficient resource allocation.
ERP Programs in Services
In the services industry, ERP programs help manage projects, streamline financial operations, and improve overall service delivery. This contributes to enhanced client satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ERP programs serve as transformative tools for businesses, offering a holistic approach to business management. From streamlined processes to improved decision-making, they prove to be invaluable assets in the competitive landscape of modern enterprises.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Is ERP software suitable for small businesses?
Yes, many ERP programs offer scalability, making them suitable for businesses of all sizes.
- How long does it take to implement an ERP program?
Implementation times vary, but thorough planning and training can expedite the process.
- Can ERP programs be customized to fit unique business processes?
Yes, ERP programs are often customizable to align with specific business requirements.
- What sets ERP programs apart from other business management solutions?
ERP programs offer a comprehensive suite of tools covering various business functions, providing a holistic approach to management.
- How does ERP software address security concerns?
ERP software employs data encryption and role-based access control to ensure robust security measures.